I used to think that Apple's use of HEIF (High Efficiency Image File Format) was for supporting its Live Photo feature. However, both I and the Internet were mistaken.
When you connect your iPhone to a PC or a Mac and check its album folder, you will find that Apple stores Live Photos in two separate files: an HEIC file and a MOV file.
HEIC stands for High Efficiency Image Container, a variant of HEIF that stores static photos. The MOV file format is used to store videos in the HEVC (High Efficiency Video File Format).
That's it. The Live Photo is just a combination of a static photo with a short video.
So, can I make a live photo?
Now that we have a grasp of how Live Photos works, can we merge any still photo with a random short video to create a "Live Photo" in the iOS album?
My first attempt was to change the filename of both a photo and a video to be identical. Then, dragging them into the macOS Photo App. However, the app failed to recognize them as live photos. Of course, it's not that easy.
After reading the documents, I found a rule in the "metadata" field of both the image and the video: a magical number called “identifier” in these two files should be the same.
The information is outdated. Previously, Apple stored a live photo using a JPG file and a H.264 video file. They have now upgraded to using a HEIC file and a H.265 video file.
But anyway, let’s check the old rules first, and see if they still apply to new formats.
A live photo has two resources. They are tied together with an asset identifier (a UUID as a string).
- A JPEG; this must have a metadata entry for
kCGImagePropertyMakerAppleDictionarywith[17 : assetIdentifier](17 is the Apple Maker Note Asset Identifier key).
- A Quicktime MOV encoded with H.264 at the appropriate framerate (12-15fps) and size (1080p). This MOV must have:
- Top-level Quicktime Metadata entry for
["com.apple.quicktime.content.identifier" : assetIdentifier]. If usingAVAssetyou can get this fromasset.metadataForFormat(AVMetadataFormatQuickTimeMetadata) - Timed Metadata track with
["com.apple.quicktime.still-image-time" : 0xFF]; The actual still image time matches up to the presentation timestamp for this metadata item. The payload seems to just be a single0xFFbyte (aka -1) and can be ignored. If using anAVAssetReaderyou can useCMSampleBufferGetOutputPresentationTimeStampto get this time.
The
assetIdentifier is what ties the two items together and the timed metadata track is what tells the system where the still image sits in the movie timeline.Excellent! Let's quickly create a prototype. I think adding a metadata field is actually more difficult than modifying an existing one. Therefore, our goal is to swap the video part of two live photos.
First I took two live photos using my iPhone (13 Pro, iOS 17.0), and export them as separated HEIC and MOV files.
Let's write a Swift script to fetch metadata from HEIC photos. Swift is much more efficient in handling HEIC photos compared to Python, as I discovered after spending two hours struggling with Python libraries.
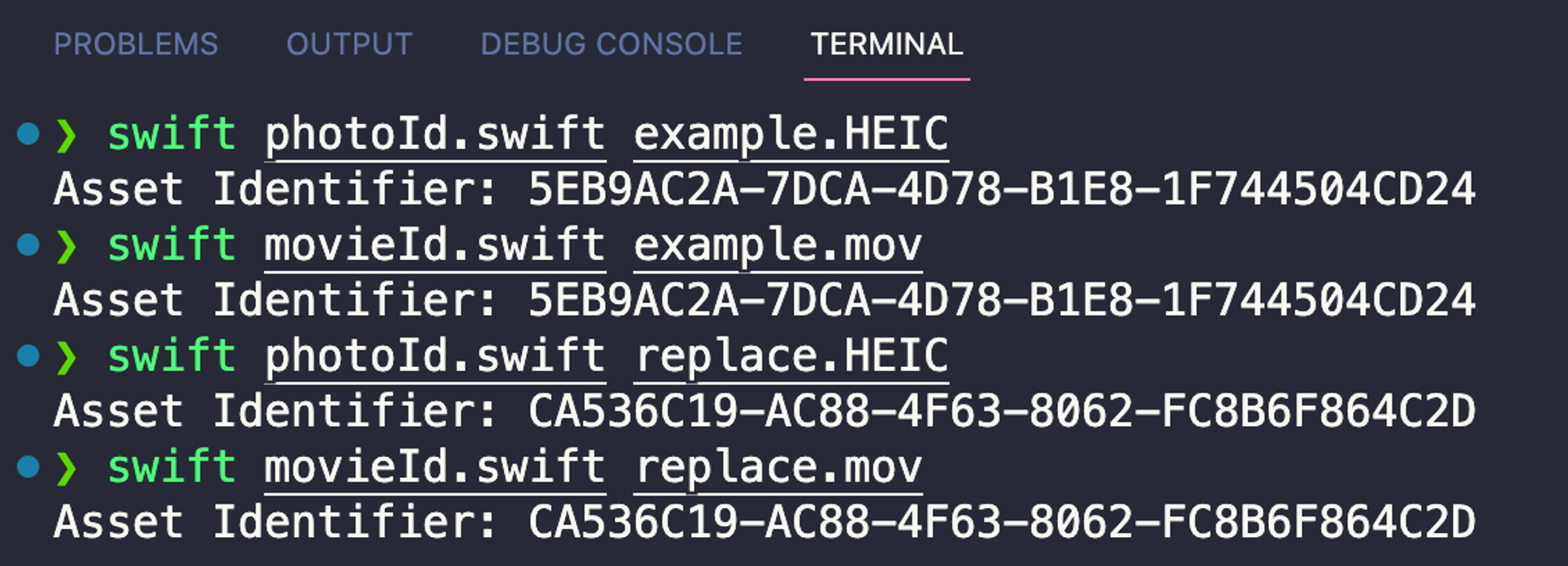
import Foundation import ImageIO func fetchAssetIdentifier(fromHEICPhotoAtPath path: String) -> String? { let imageSource = CGImageSourceCreateWithURL(URL(fileURLWithPath: path) as CFURL, nil) let imageProperties = CGImageSourceCopyPropertiesAtIndex(imageSource!, 0, nil) as? [CFString: Any] let appleMakerDict = imageProperties?[kCGImagePropertyMakerAppleDictionary] as? [CFString: Any] for (key, value) in appleMakerDict! { if key as String == "17" { return value as? String } } return nil } let heicFilePath = "example.HEIC" let assetIdentifier = fetchAssetIdentifier(fromHEICPhotoAtPath: heicFilePath)! print("Asset Identifier: \(assetIdentifier)")
Let's write another Swift script to fetch metadata from MOV files. It's unfortunate that ChatGPT only has knowledge up until 2019, as writing Swift code can be challenging due to Apple's annual annoying API changes. Luckily, I still have GitHub Copilot Chat, which is great for development purposes.
import AVFoundation import Foundation func fetchAssetIdentifier(fromURL url: URL) async -> String? { let asset = AVAsset(url: url) let metadata = try! await asset.loadMetadata(for: AVMetadataFormat.quickTimeMetadata) // ꜛ await here // HEIC metadata loading is synchronized // but MOV must be asynchronous. Who could have predicted that? for item in metadata { let key = item.commonKey?.rawValue let value = try! await item.load(.value) if key == "identifier" { return value as? String } } return nil } let movieFilePath = CommandLine.arguments[1] let movieURL = URL(fileURLWithPath: movieFilePath) let assetIdentifier = await fetchAssetIdentifier(fromURL: movieURL) print("Asset Identifier: \(assetIdentifier!)")
And I got the same asset identifier, the rules still apply.
To swap the video portion in these two live photos, we can modify either the identifier in HEIC or MOV. For simplicity's sake, let's attempt to modify the HEIC file. Add another function.
import Foundation import ImageIO func modifyAndSaveHEICPhoto(atPath path: String, assetIdentifier: String) { let imageSource = CGImageSourceCreateWithURL(URL(fileURLWithPath: path) as CFURL, nil) let imageProperties = CGImageSourceCopyPropertiesAtIndex(imageSource!, 0, nil) as? [CFString: Any] var modifiedProperties = imageProperties! var appleMakerDict = modifiedProperties[kCGImagePropertyMakerAppleDictionary] as? [CFString: Any] appleMakerDict?["17" as CFString] = assetIdentifier modifiedProperties[kCGImagePropertyMakerAppleDictionary] = appleMakerDict let newImageData = NSMutableData() let destination = CGImageDestinationCreateWithData(newImageData, CGImageSourceGetType(imageSource!)!, 1, nil)! CGImageDestinationAddImageFromSource(destination, imageSource!, 0, modifiedProperties as CFDictionary) CGImageDestinationFinalize(destination) let newFilePath = (path as NSString).deletingPathExtension + "_modified.HEIC" newImageData.write(toFile: newFilePath, atomically: true) print("Modified photo saved at: \(newFilePath)") } let heicFilePath = CommandLine.arguments[1] let assetIdentifier = CommandLine.arguments[2] modifyAndSaveHEICPhoto(atPath: heicFilePath, assetIdentifier: assetIdentifier)
This function can modify the identifier in HEIC photos to the constant string value in
modifiedAssetIdentifier.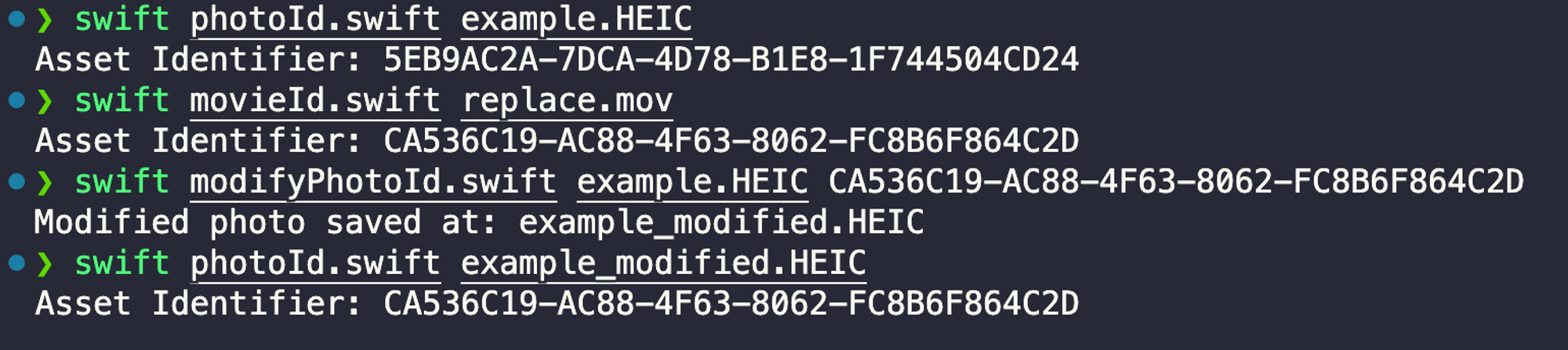
OK, now change the filename of
replace.mov to example_modified.HEIC.Drag both of
example_modified.HEIC and example_modified.mov into macOS Photo App, and — boom! We have a swapped new live photo.